随着中国的各种实力的提高,经常在各种媒体上看到中国与各个国家历年的各种指标数据的对比,为了更清楚的展示历年的发展趋势,有的还做成了动图,看到中国各种指标数据的近年的不断逆袭,心中的自豪感油然而生。今天通过Python来实现matplotlib的动态绘图,将中美两国近年的GDP做个对比,展示中国GPD对美国的追赶态势,相信不久的将来中国的GDP数据将稳超美国。
效果如下: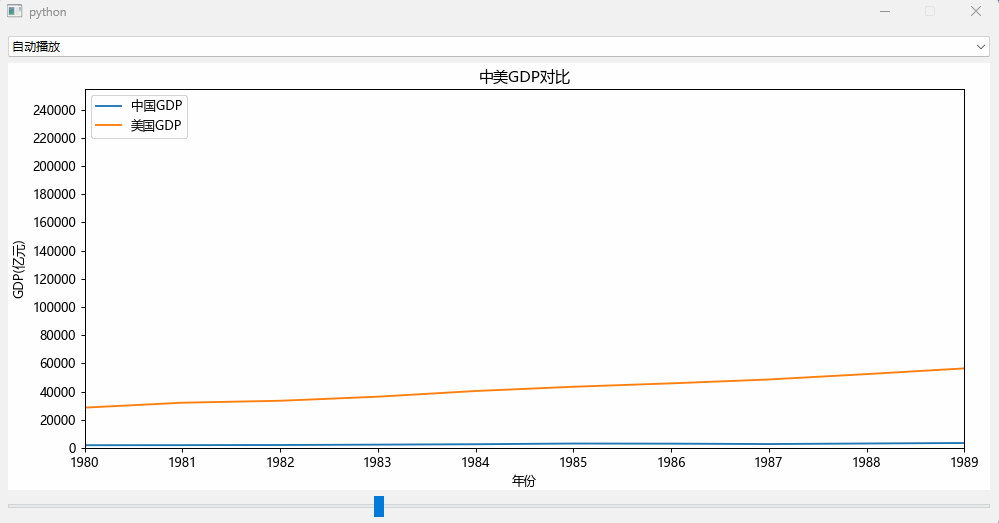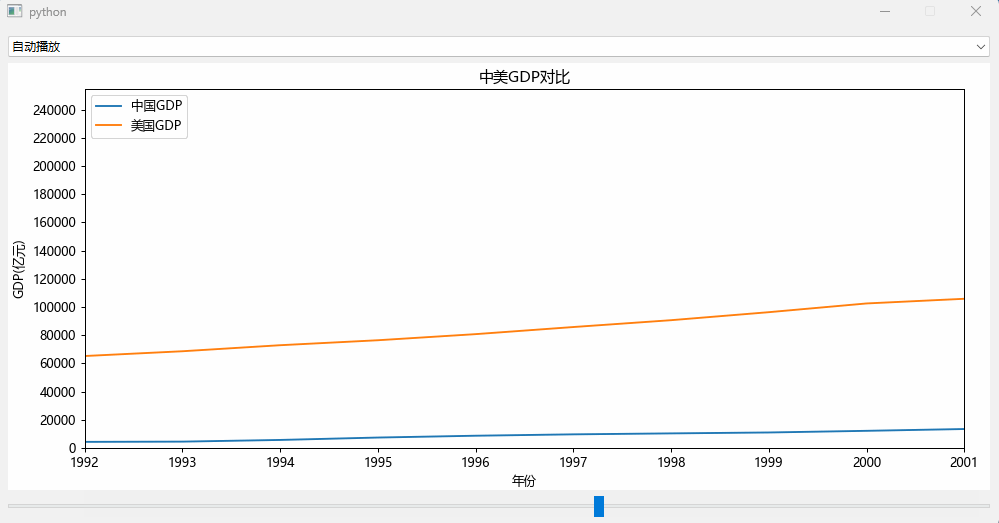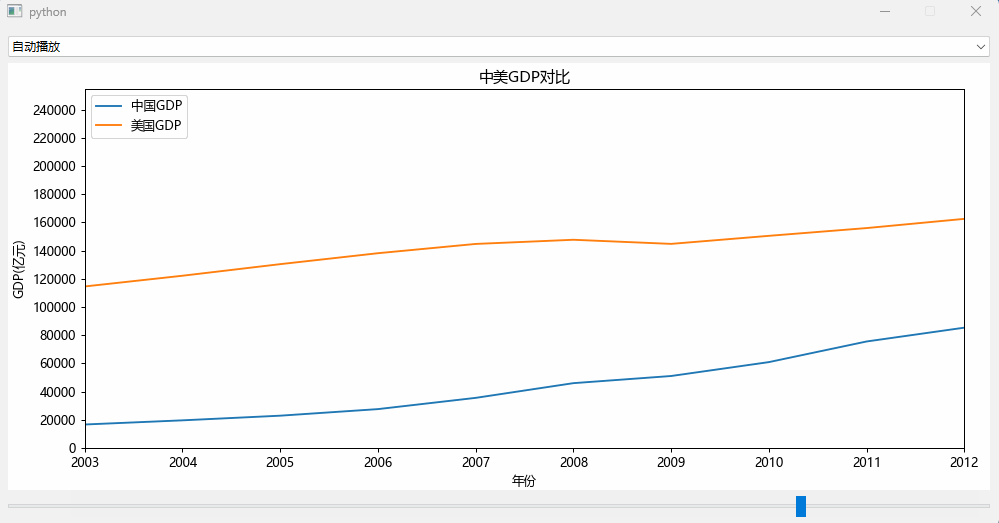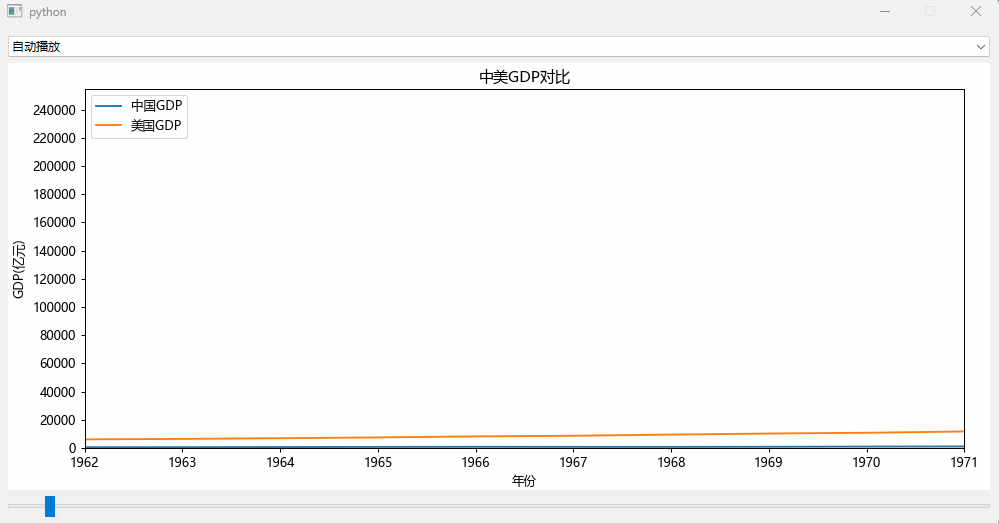
实现上面的动态绘图效果,综合用到了pandas的数据采集、数据整理、matplotlib绘图、坐标轴及数据的动态定义、定时器等知识。最终通过Python的GUI库PySide进行展示形成一个GUI的可执行程序。
一、数据采集和准备
中美历年的GDP数据通过百度在网上一搜一大把。我是从https://www.kylc.com/stats/global/yearly_per_country/g_gdp/chn-usa.html 找到的数据。将数据整理成EXCEL保存至data\中国VS美国.xlsx。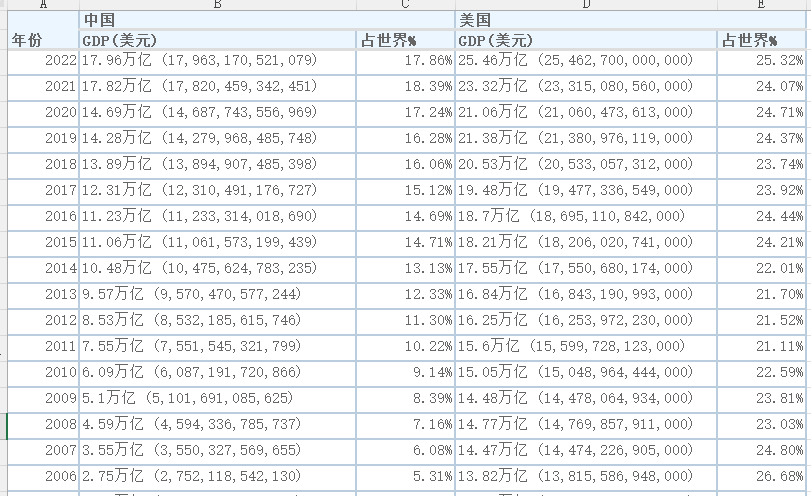
有从1966年至2022年的中美GDP的数据。
首先对这些数据进行整理,因为获取的GDP数据是字符串类型如17.96万亿 (17,963,170,521,079),我们需要将GDP的数据从文本中提取出来,也就是取括号中的数据。
这里通过正则表达式将括号中的GDP数据提取出来,并转换为亿元为单位。
1 | import re |
有了数据以后就可以通过数据绘图了。
二、matplotlib绘图
先通过matplotlib绘图看看数据的效果。
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
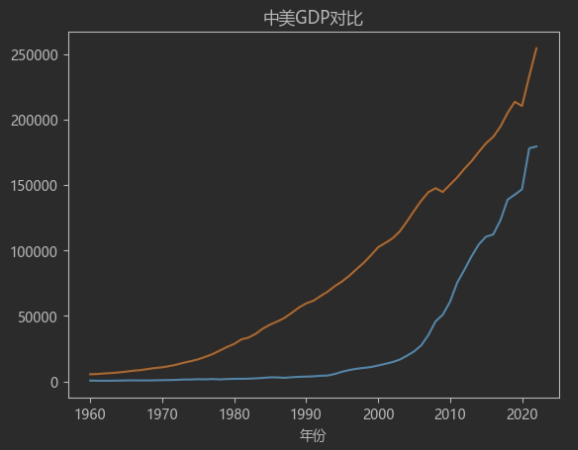
可以看到中国的GDP数据在1960年至1990年都是比较平稳的,到了1990年后中国开始了爆发式的追赶模式。
我们要将这种趋势通过动态的方式展示出来。
三、数据展示与动态更新
首先通过QMainWindw定义QWidget组件,在QWidget中加入FigureCanvasQTAgg组件通过canvas载入matplotlib绘图。
1 | class ApplicationWindow(QMainWindow): |
一种方式是通过QSlider组件,通过手动拉slider组件来实现数据的变化,一种通过QTimer组件自动让数据变化。
1、QSlider组件,手动方式实现动态绘图
1 |
|
手动拉slider组件来实现数据的变化效果: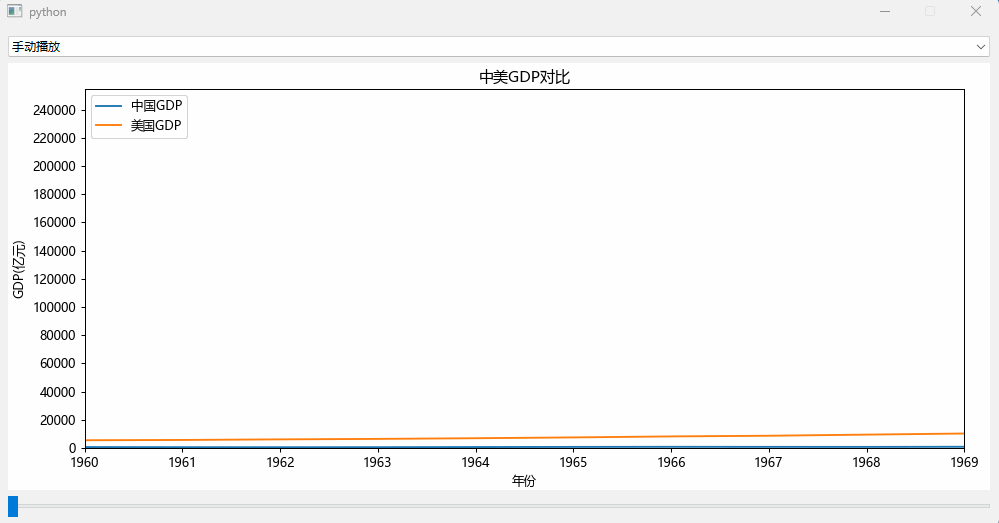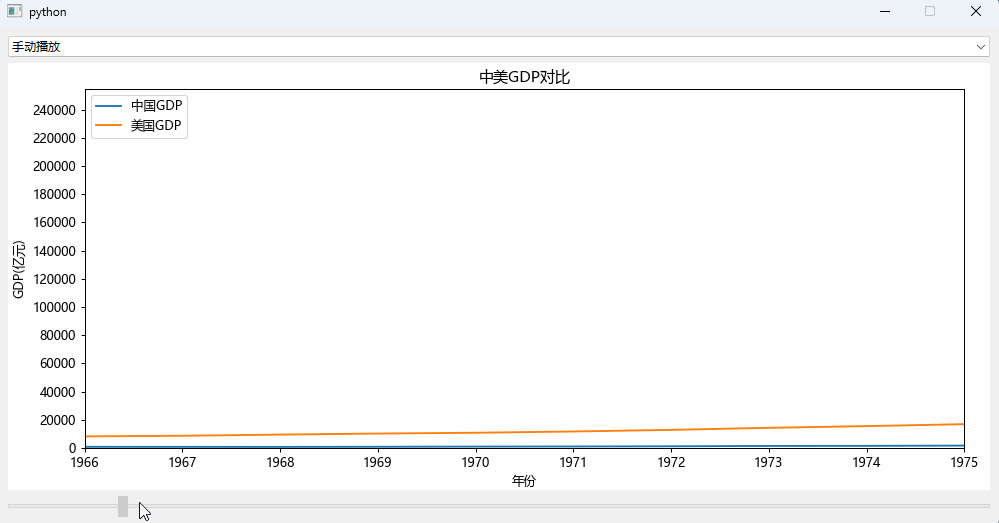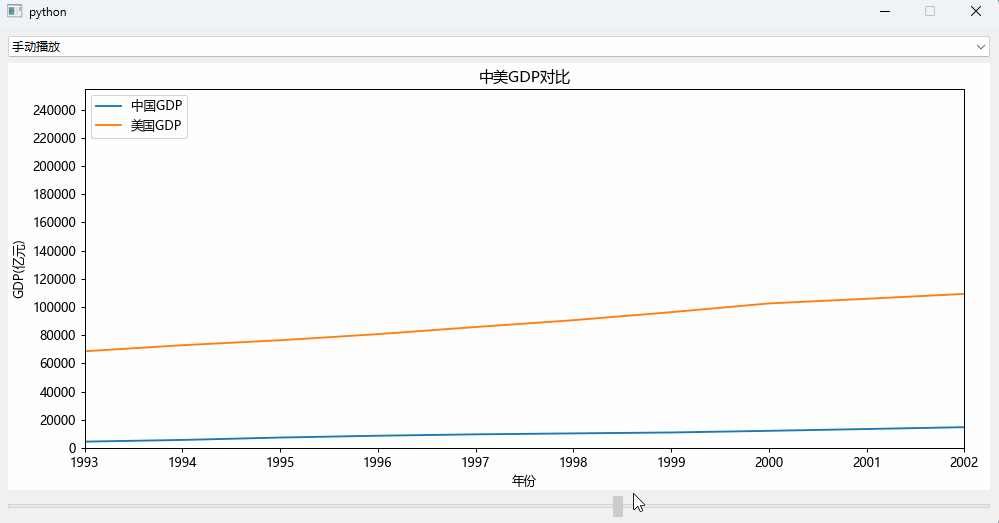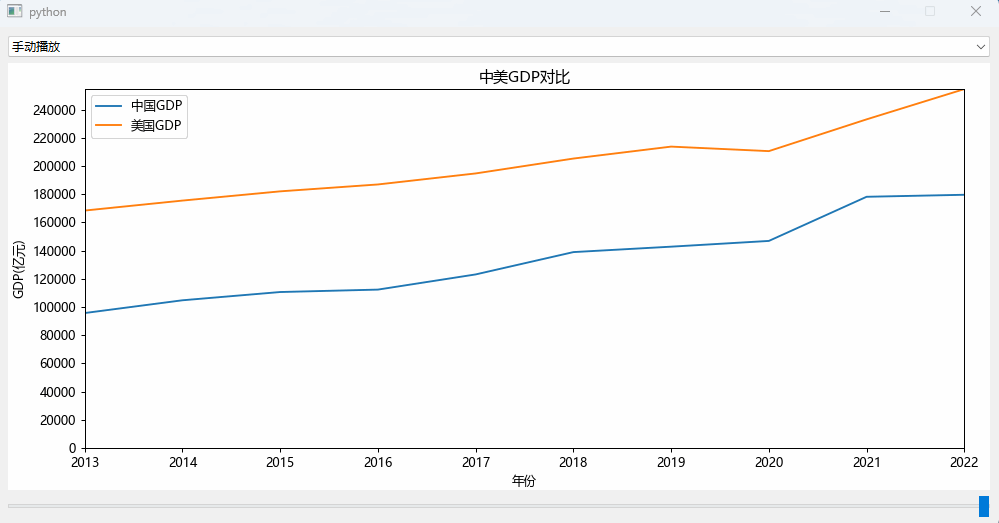
2、QTimer组件,自动动态绘图
1 | self.autoslider() |
效果如文章最前面所示。
四、完整代码
1 | import re |
六、总结
Python实现matplotlib动态绘图,是非常简单和容易的,其实关键还是在数据的组织,也就是要准备好要绘图的坐标轴的x的数据和y的数据,通过set_data(x,y)来动态更新数据,要注意的是变化的数据后X轴或Y轴的显示要变化,这里可以通过轴的set_xlim()或set_ylim()方法来动态设置,刻度也可通过set_major_locator()来指定。
数据集见 https://xiejava1018.github.io/xiejavaimagesrc/images/2023/20230827/中国VS美国.xlsx
作者博客:http://xiejava.ishareread.com/

关注微信公众号,一起学习、成长!